For graduating class of 2024, 2025 or 2026

Training in the facilities of the Texas Medical Center, the world's largest medical complex, presents you with a variety of settings and patient populations that is hard to match anywhere in the world. Exposure to a variety of clinical settings and patient populations throughout your clinical rotations will prepare you to succeed in any situation your career presents.
Core Clerkships
The clinical curriculum begins in January of your second year. This phase of your training uses patient-centered learning techniques, which include taking histories, performing physical examinations, reviewing laboratory results, and working with faculty physicians to manage patients through diagnosis and treatment.
The Clinical Years
The charts below show an M.D. students typical path through the clinical curriculum.
Year 2 - Spring
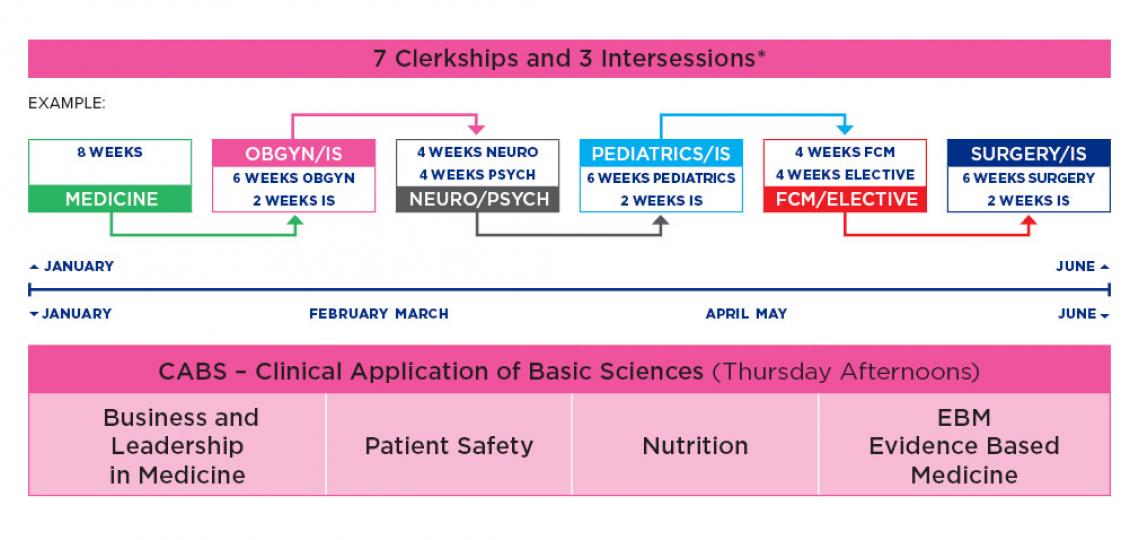
Year 3 - Fall

Year 3- Spring
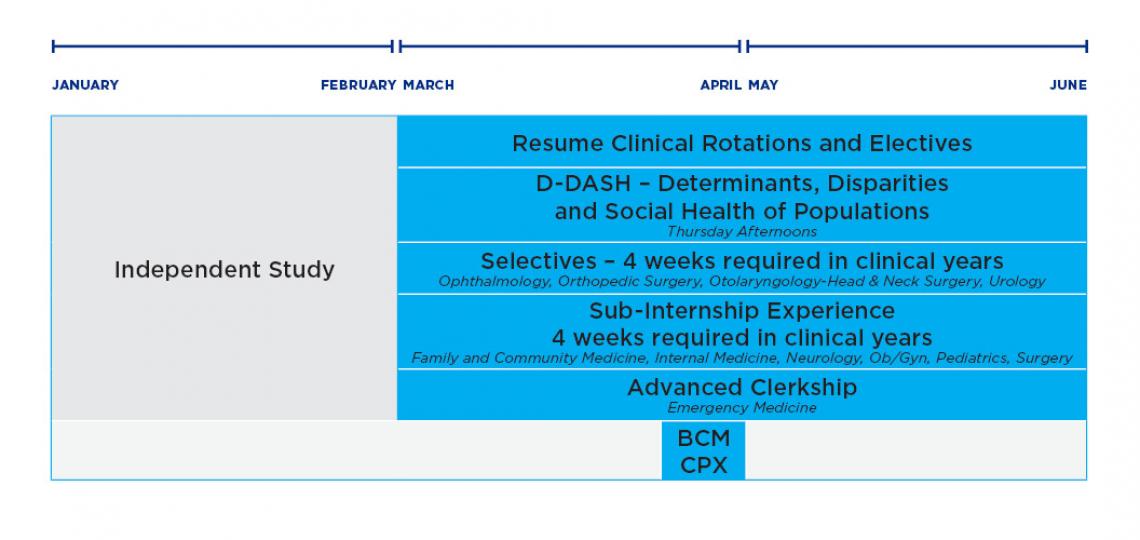
Year 4 - Fall to Spring
Customizing Your Education
You may tailor your clinical experience to your interests by pursuing other specialties through rotations called “selectives," a sub-internship, and through lots of electives.
Pathways span the four years of medical school and include both classroom, clinical and/or research activities in the specific areas of interest.
Clinical Sciences Course Descriptions
The required courses within the clinical curriculum provide you the opportunity to build skills and explore various issues.
* Course credits pertain to 2024-2025 academic year.
APEX: MCAPX-MAIN
The goal of this course is to promote the transition of a knowledgeable fourth year graduating student to a professional physician in training. The course allows students to individualize the educational experience to meet their personal interests and needs. It offers a unique, practical and interactive focus on solidifying students' medical school experiences while developing and fine-tuning skills that will help them enter their internship and residency with confidence.
Credits: 2.0
Course Director: Uma Ayyala, M.D.
Associate Course Director: Loan Nguyen, M.D.
Determinants, Disparities, and Social/Population Health (DDASH): MCDSH-MAIN
The goal of DDASH is to familiarize medical students with upstream social and structural factors that influence health outcomes in patients. Students learn to appraise social determinants of health, consider elements of healthcare access, economic instability, social support, community cohesion, etc. and deliberate on policies that seed health disparities through these domains. This lens explores the roots of existing health inequities while reviewing intersecting anthropological and social paradigms that form the backdrop of mistrust in healthcare, chronic disease, homelessness, addiction, etc. The course uses team projects, simulation exercises, and case studies guiding students to recognize, appropriately screen, and expand management plans for unmet social needs in patients, thereby increasing the impact of their clinical practice. Students participate in dedicated discussions on implicit bias within healthcare and gain exposure to bias reduction strategies effective for delivering culturally appropriate medical care. Examining these premises, directly or indirectly, aims to foster the development of professional attributes of integrity, respect, inclusion, compassion, justice, and empathy that are foundational for building awareness, attitude, and advocacy for equitable healthcare.
Credits: 2.5
Course Director: Malvika Juneja, M.D.
Associate Course Director: Victoria McCurry, M.D.
Practice of Medicine (POM) III: Synthesis: MBPM3-MAIN
In this course, students will apply the foundational medical knowledge and clinical skills learned in their first year to patients in the inpatient setting with a focus on hypothesis-driven data collection, verbal and written communication skills, and clinical reasoning. In this course, large group interactives will help students begin to build differential diagnoses for common presenting complaints for hospitalized patients and to developed illness scripts for common diagnoses. Students will also work with a clinical preceptor in small groups, perform complete history and physical examinations on hospitalized patients, deliver organized verbal patient presentations, and complete written H&Ps. The goal of this course is to help students to synthesize the knowledge and skills acquired in their first year such that they are prepared to begin their inpatient clerkships.
Credits: 2.00
Course Director: Catherine Daniel, M.D.
Associate Course Directors: Fabrizio Canepa, M.D. and Andrew Hawrylak, M.D.
Transitions to Clerkships: MBITC-MAIN
Transitions to Clerkships aims to prepare students to succeed in the clinical learning environment. In the course, students will refine their clinical skills and implement principles of clinical reasoning. They will learn and apply standards of professionalism and ethics. Students will leave the course with an improved understanding of the expectations of ward clerks, enhanced skills for self-regulated learning, and tools to promote personal wellness during clerkships and beyond.
Credits: 4.5
Course Director: Anita Kusnoor, M.D.
Associate Course Director (Houston): Meghan McClure, M.D.
Associate Course Director (Temple): Samantha Allen, M.D.
Requirements
View requirements for Degree Doctor of Medicine and Core Competency Graduation Goals.
Compact
View Compact Between Teachers, Learners and Educational Staff.
Progress Notes
Progress Notes is the student magazine of Baylor College of Medicine. In it, students of the College share their stories from the clinics, their thoughts on medicine and healthcare, and stories from the frontlines of research.
Glued feet: The importance of compassion and healing in medicine
Read this third-year medical student's reflections on a patient encounter that led to the realization that simple acts of compassion can have a significant impact on a patient and a physician.
The article is published in Progress Notes, the student magazine of Baylor College of Medicine. In it, students of the College share their stories from the clinics, their thoughts on medicine and healthcare, and stories from the frontlines of research.

Growing pains: Clinical training during COVID-19
A third-year medical student at Baylor College of Medicine reflects on hospital training during COVID-19. Read the article.