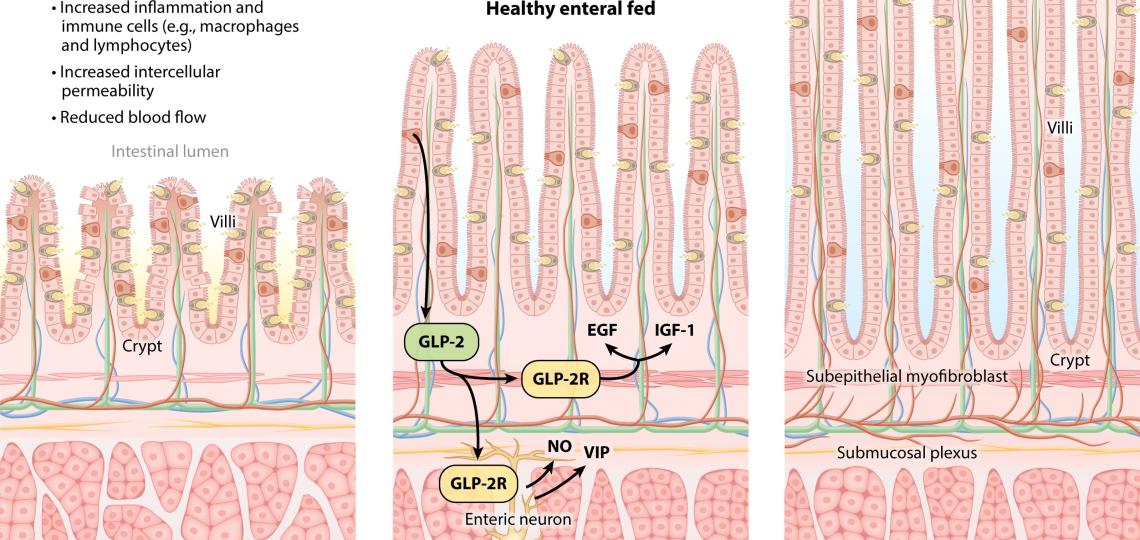
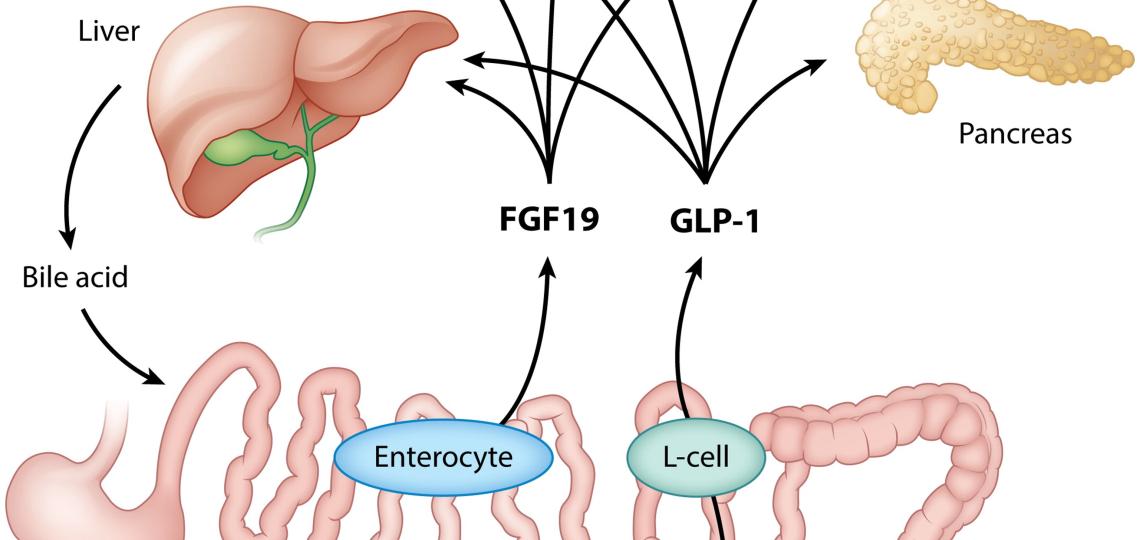
Past projects in the laboratory have been aimed at establishing the adverse effect of TPN on intestinal growth and development. Also the cellular and physiological functions of enteral nutrition and the secretion of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2), an FDA-approved gut hormone for treatment of adult short-bowel syndrome. Several of our studies described how TPN results in intestinal atrophy and loss of function. We also were first to show the trophic and vasoactive actions of GLP-2 in the neonatal gut. We identified the cellular co-localization of the GLP-2 receptor in enteric neurons with neurotransmitters. We have also investigated how enteral nutrients trigger secretion of fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19), a novel enterokine involved in bile acid homeostasis.