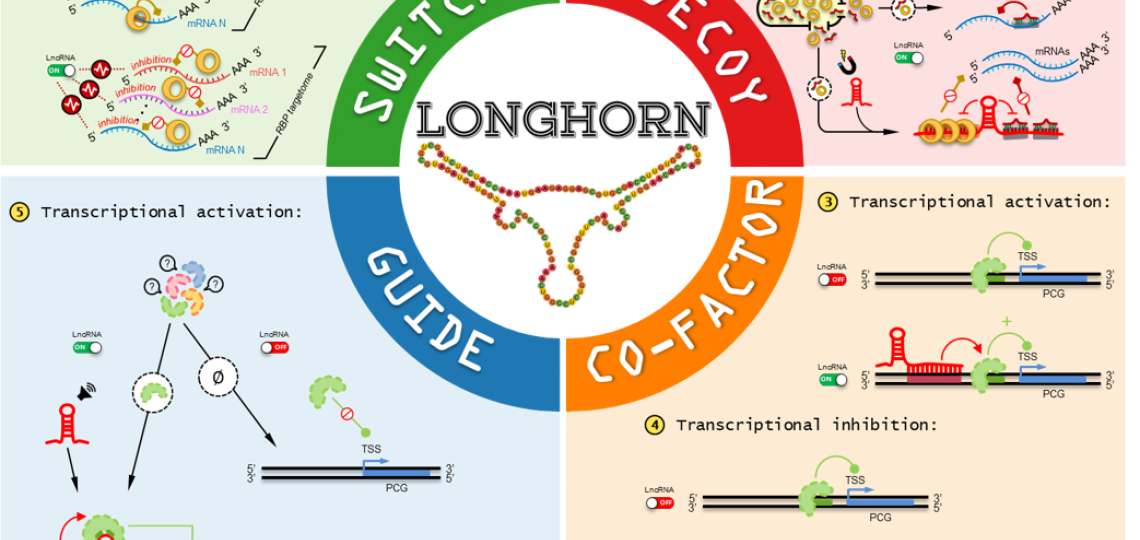
LongHorn predicts lncRNA targets
Pan-cancer analyses of LongHorn-predicted lncRNA regulatory interactions suggest that the dysregulation of hundreds of lncRNAs target and alter the expression of cancer genes and pathways in each tumor context. This implies that hundreds of lncRNAs can alter tumor phenotypes in each tumor context.
About the Lab
In the Regulatory Circuits Lab we infer pathophysiological consequences of genomic variants and aberrant gene expression through analyses of molecular profiles. Towards this goal we combine computational analyses and biochemical experiments, leveraging regulatory circuits to identify new driver genes and genomic variants that act in cis or in trans. We develop methods for inferring alterations, improving expression estimates from RNA-seq data from various tissues and using various extraction methods, and inferring clonal cell populations and driving alterations based on profiles of related samples including multiple biopsies from the same patient that are taken from multiple tumor sections and before and after treatment.
Hermes Predicts Modulators of microRNA Activity
Genome-wide inference of microRNA modulators identified a post-transcriptional regulatory network in GBM that was predictive of aberrant expression of GBM driver genes.

Cupid Predicts microRNA Targets
Cupid microRNA-target prediction was verified using high-throughput protein expression experiments.
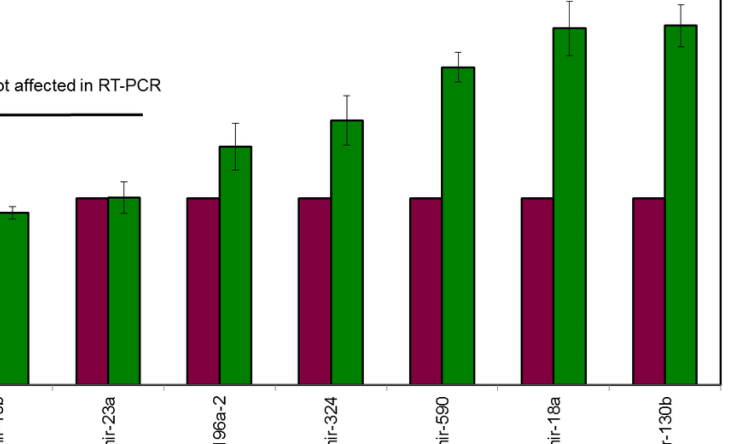
Trident Predicts microRNA Biogenesis Regulators
Trident identified a new microRNA biogenesis regulator whose amplification alters microRNA regulatory programs in cancer.

PCI is a Pan-cancer Network of microRNA Modulators
MicroRNA modulators in the PCI network were predictive of missing genomic variability of cancer genes in 18,000 tumor profiles obtained from 139 patient cohorts.