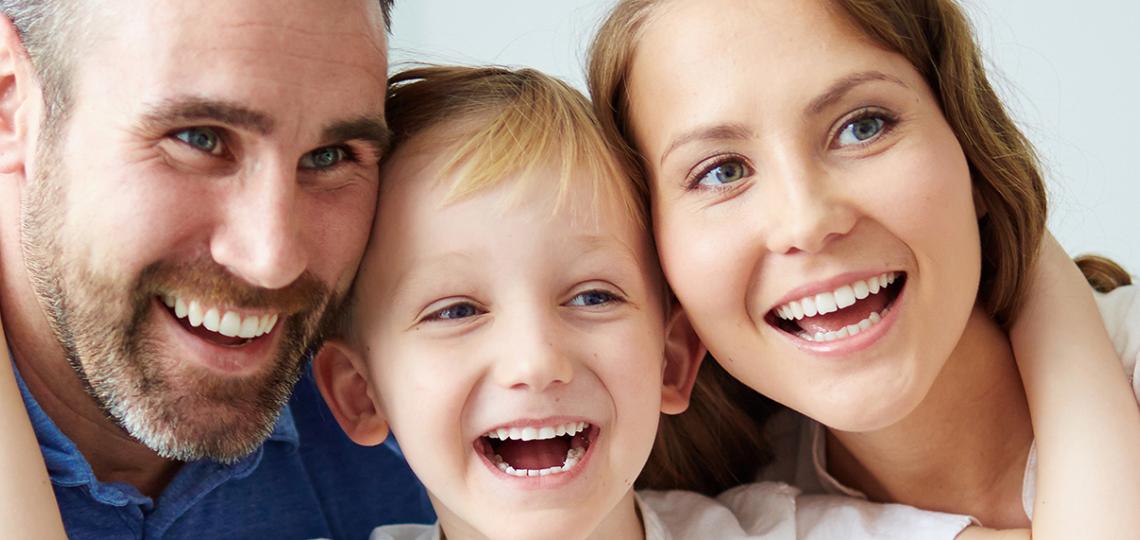
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. UTIs are usually caused by bacteria, but they can also be caused by fungi and, in rare cases, by viruses.
The symptoms of a UTI can vary depending on which part of the urinary tract is infected. Here are some common symptoms:
- Burning sensation during urination
- Frequent urination
- Frequent urge to urinate, but incomplete voiding
- Pain or pressure in the back or lower abdomen
- Pelvic pain
- Blood in urine
- Cloudy, dark, or strange or strong-smelling urine, mixed with blood in some cases
- Tiredness
- Fever and/or chills
- Nausea and/or vomiting
Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are diagnosed using a combination of patient symptoms, medical history, and laboratory tests.
Medical History and Symptoms: The doctor will first examine the symptoms and note the medical history.
Urine Analysis: This is a test to check for the presence of organisms causing infection in the urine.
Urine Culture: This test is done to identify the type of organism causing the infection.
Imaging Tests: In some cases, if there are abnormalities suspected in the urinary tract or if the infections are recurrent, imaging tests like a CT scan or an MRI of the abdomen might be performed to provide a detailed image of the urinary tract.
Cystoscopy: In certain cases, a long tube-like instrument might be used to view the inside of the urethra and urinary bladder.
What are the treatments for a urinary tract infection?
After the diagnosis, treatment typically involves antibiotics. The type of antibiotic, its dosage, and duration depends on the type of organism and severity of the infection. It’s also recommended to drink plenty of water to flush out the germs and use heating pads to get relief from back pain.
Please note that this is a general process and the exact diagnostic process can vary depending on the individual’s symptoms and medical history. Always consult with a healthcare provider for accurate information.