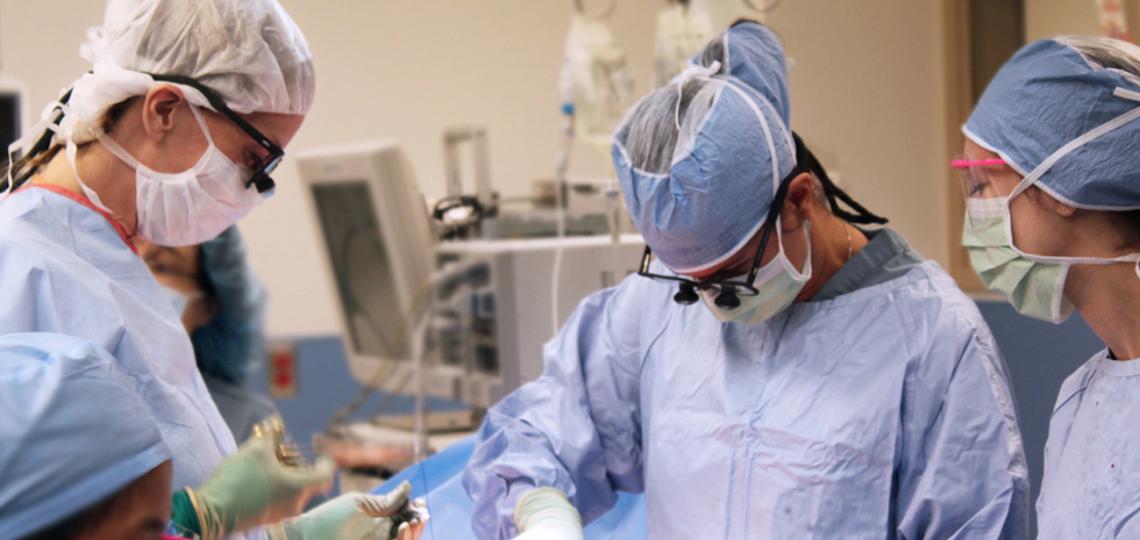
Mastectomy is when all breast tissue is removed. In appropriately selected patients, the surgeon may be able to conserve some of the skin and/or nipple normally lost during a mastectomy.
The choice of what surgery is best for you can be a difficult decision to make. After reviewing your diagnosis in clinic, the breast surgeon can work with you to arrive at a shared decision that balances your peace of mind, your cosmetic expectations as well as the treatment for your breast cancer.
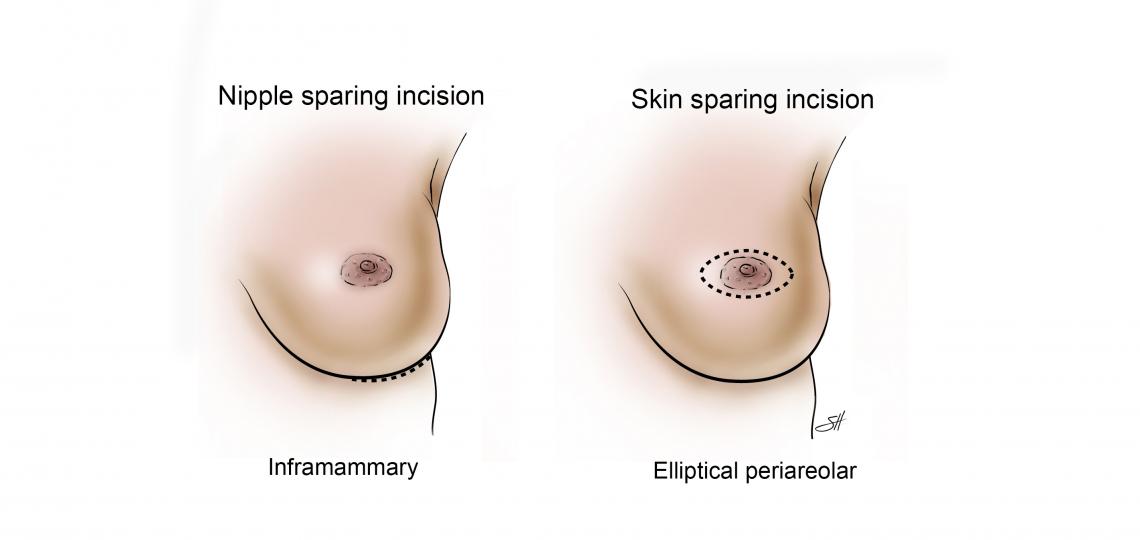
Nipple and Skin-Sparing Mastectomy
During a nipple-sparing mastectomy, the breast tissue is removed, while all of the skin and the nipple and areola are left intact. During skin-sparing mastectomy, the nipple and areola are removed along with the breast, but only a small amount of skin is removed.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
The most common reason for a mastectomy is breast cancer.
Mastectomy is when all breast tissue is removed. In appropriately selected patients, the surgeon may be able to conserve some of the skin and/or nipple normally lost during a mastectomy.
The choice of what surgery is best for you can be a difficult decision to make. After reviewing your diagnosis in clinic, the breast surgeon can work with you to arrive at a shared decision that balances your peace of mind, your cosmetic expectations as well as the treatment for your breast cancer.
Women who have a very high risk of developing breast cancer may choose to have a risk-reducing procedure, commonly referred to as a prophylactic mastectomy.
You may be more likely to get breast cancer if one or more close family relatives has had the disease, especially at an early age. Genetic tests (such as BRCA1 or BRCA2) may help show that you have a high risk.
Prophylactic mastectomy should be done only after very careful thought and discussion with your doctor, a genetic counselor, your family, and loved ones.
Mastectomy greatly reduces the risk of breast cancer, but does not eliminate it.
 Credit
Credit
After Surgery
Most women stay in the hospital overnight after a mastectomy, but this depends largely on your health status and if you will be undergoing reconstruction.
All patients that undergo mastectomy will have drains post-operatively. The drains are eventually removed in clinic.
You may have pain around the site of your incision after surgery. The pain is usually moderate after the first day and slowly becomes less during the next few weeks. You will receive pain medicines before you are released from the hospital.