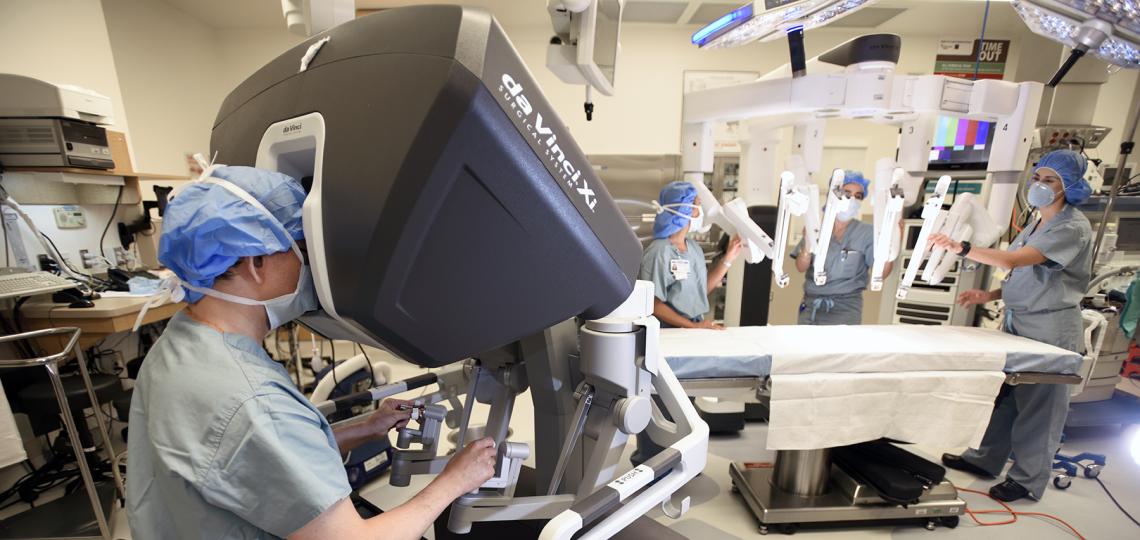
Robotic heart surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that utilizes robotic arms to perform surgery on the heart. The robotic arms are controlled by a surgeon who operates from a console in the operating room. This technique is used to treat a wide range of heart conditions, including coronary artery disease and valve disease.
Patients who are candidates for robotic heart surgery are typically those who are at high risk for traditional open-heart surgery. This can include patients who are older, have other medical conditions, or who have previously had heart surgery. The robotic approach is particularly beneficial in these cases because it is less invasive and leads to a shorter recovery time.
One of the main benefits of robotic heart surgery versus open surgery is that it is a less invasive procedure. This means that there are smaller incisions, less blood loss, and a shorter hospital stay. Patients who undergo robotic heart surgery also tend to experience less pain and scarring than those who have open surgery.
Robotic heart valve surgery in particular, offers a number of benefits over traditional heart valve surgery. The robotic instruments can access the heart through small incisions, which means less pain and a shorter recovery time for the patient. Additionally, because the robotic arm is so precise, the surgeon is able to perform the surgery with greater accuracy, which can lead to better outcomes.
Recovery
Recovery from robotic heart surgery tends to be quicker and easier and patients typically spend less time in the hospital and are able to return to their normal activities more quickly than with open surgery.